What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 4
catanddoghelp
Nov 30, 2025 · 14 min read
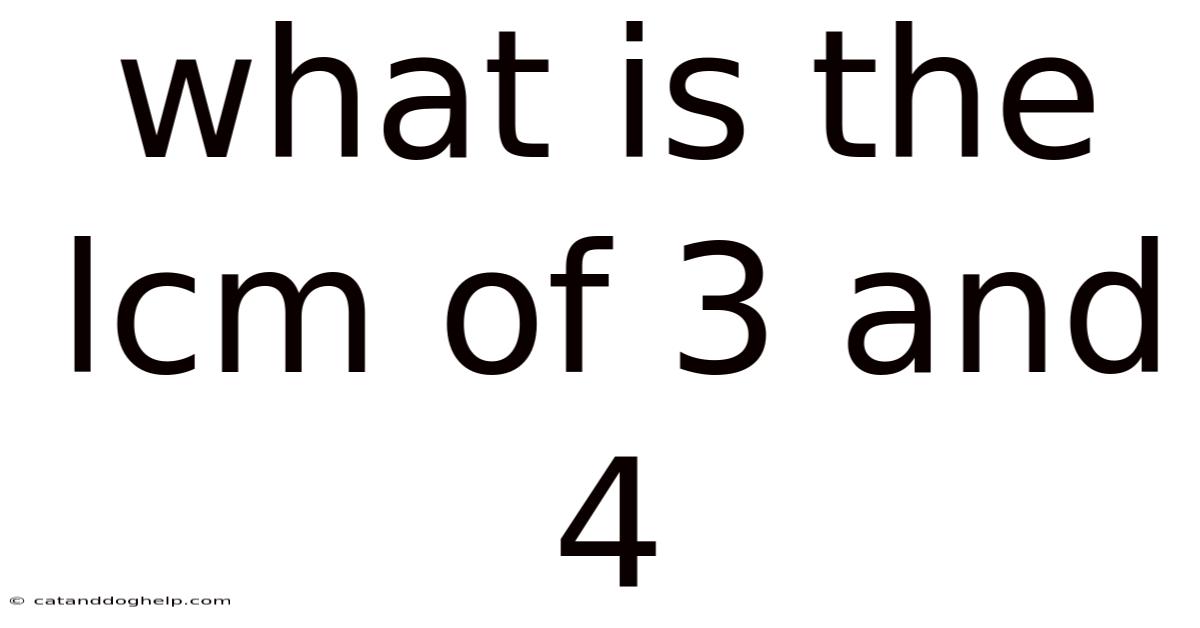
Table of Contents
Have you ever tried dividing up snacks equally among friends, only to find yourself stuck with leftovers? Or perhaps you've tried scheduling meetings with colleagues in different time zones and struggled to find a time that works for everyone? These everyday scenarios often require a common mathematical concept: the Least Common Multiple. Understanding this concept can simplify many real-world problems, from cooking to project management.
Imagine you are tiling a floor using rectangular tiles that are 3 inches wide and 4 inches long. You want to arrange the tiles to form a square without cutting any tiles. How big should the square be? The answer lies in finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 3 and 4. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both 3 and 4. Determining the LCM helps you figure out the dimensions of the smallest square you can create with these tiles. This simple example demonstrates how the LCM is not just an abstract mathematical concept but a practical tool that can help solve tangible problems. Let’s explore what exactly the LCM of 3 and 4 means and how to find it.
Main Subheading: Understanding the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in number theory, providing a way to find the smallest positive integer that is divisible by two or more numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that each of the given numbers can divide into evenly. For instance, if you're trying to find the LCM of 3 and 4, you're looking for the smallest number that both 3 and 4 can divide into without leaving a remainder. This concept is particularly useful in various mathematical problems, such as simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and even in practical real-world scenarios like scheduling and resource allocation.
The LCM isn't just a theoretical tool; it has numerous applications in everyday life. Consider the problem of scheduling two events that occur at different intervals. For example, one event might occur every 3 days, while another occurs every 4 days. Finding the LCM of 3 and 4 helps you determine when both events will occur on the same day. This is crucial for coordinating schedules, planning projects, and managing resources efficiently. Similarly, in cooking, the LCM can help you adjust recipes when scaling up or down, ensuring that all ingredients are in the correct proportions. The LCM serves as a bridge between abstract mathematics and practical problem-solving, making it an essential concept for anyone looking to simplify and optimize their daily tasks.
Comprehensive Overview
Definition of Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by each of the given integers. Divisibility means that when the LCM is divided by any of the given numbers, the result is a whole number with no remainder. To illustrate, let’s find the LCM of two numbers, say a and b. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both a and b. Mathematically, if LCM(a, b) = x, then x is the smallest positive integer such that x is divisible by a and x is divisible by b.
Scientific Foundations
The concept of the LCM is rooted in number theory, a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of numbers. It is closely related to the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD), also known as the Highest Common Factor (HCF). The GCD of two numbers is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The LCM and GCD are connected by the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a| * |b|) / GCD(a, b)
This formula shows that the LCM can be calculated using the GCD, and vice versa. The GCD is often easier to compute using algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm, which provides an efficient way to find the GCD of two numbers. Understanding these scientific foundations helps in applying the LCM effectively in various mathematical and computational contexts.
Historical Context
The concept of the LCM has been used since ancient times, with evidence of its application in early mathematical texts from various cultures. Ancient civilizations used multiples and divisors in practical problems such as land division, calendar construction, and astronomical calculations. The formal study of number theory, including concepts like LCM and GCD, gained prominence with Greek mathematicians like Euclid, whose Elements laid the groundwork for much of modern number theory.
Over the centuries, mathematicians from different cultures have contributed to our understanding of the LCM. In ancient India, mathematicians like Aryabhata and Brahmagupta explored properties of multiples and divisors in the context of astronomy and arithmetic. In China, mathematicians developed methods for solving problems involving common multiples, which were used in calendar calculations and engineering projects. The historical development of the LCM highlights its enduring importance in mathematics and its practical applications across different civilizations.
Methods to Find the LCM
There are several methods to find the LCM of two or more numbers, each with its own advantages depending on the specific numbers involved. Here are three common methods:
-
Listing Multiples: This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. The smallest common multiple is the LCM. For example, to find the LCM of 3 and 4:
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, ...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, ...
- The smallest common multiple is 12, so LCM(3, 4) = 12.
-
Prime Factorization: This method involves finding the prime factors of each number and then taking the highest power of each prime factor that appears in any of the numbers. The LCM is the product of these highest powers. For example, to find the LCM of 3 and 4:
- Prime factors of 3: 3
- Prime factors of 4: 2^2
- LCM(3, 4) = 2^2 * 3 = 4 * 3 = 12.
-
Using the GCD: As mentioned earlier, the LCM can be calculated using the GCD with the formula: LCM(a, b) = (|a| * |b|) / GCD(a, b). To find the LCM of 3 and 4 using this method:
- GCD(3, 4) = 1 (since 3 and 4 have no common factors other than 1)
- LCM(3, 4) = (3 * 4) / 1 = 12.
Practical Examples and Applications
The LCM is used in various real-world applications, making it a valuable tool for problem-solving. Here are a few examples:
- Scheduling: As mentioned earlier, the LCM is used to determine when events occurring at different intervals will coincide. For example, if one task needs to be done every 3 days and another every 4 days, the LCM (12) tells you that both tasks will need to be done on the same day every 12 days.
- Cooking: When adjusting recipes, the LCM helps ensure that all ingredients are in the correct proportions. For example, if a recipe calls for 1/3 cup of flour and 1/4 cup of sugar, the LCM of 3 and 4 (which is 12) can be used to scale the recipe up or down while maintaining the correct ratio of ingredients.
- Tiling and Construction: When laying tiles or bricks of different sizes, the LCM helps determine the dimensions needed to create a uniform pattern without cutting any materials. For example, if you have tiles that are 3 inches wide and 4 inches long, the LCM (12) tells you that you can create a square pattern that is 12 inches by 12 inches without cutting any tiles.
- Fractions: The LCM is used to find the least common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions. This simplifies the process of combining fractions and ensures accurate results.
Trends and Latest Developments
Current Trends
In modern mathematics education, there is a growing emphasis on teaching the LCM in a way that connects it to real-world applications. Rather than just memorizing formulas, students are encouraged to explore the concept through hands-on activities, problem-solving exercises, and technology-based tools. This approach aims to make the LCM more accessible and relevant to students' lives, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of its practical uses.
Data and Popular Opinions
Surveys of mathematics educators reveal a consensus that teaching the LCM through real-world applications enhances student engagement and retention. Many educators use visual aids, interactive software, and collaborative projects to illustrate the LCM in action. For example, some teachers use online simulation tools to demonstrate how the LCM can be used to schedule events or optimize resource allocation. Others incorporate cooking recipes, construction projects, and scheduling problems into their lesson plans, allowing students to see the LCM's practical value firsthand.
Professional Insights
Experts in mathematics education emphasize the importance of building a strong foundation in number theory concepts like the LCM. They argue that understanding the LCM not only helps in solving mathematical problems but also develops critical thinking skills that are valuable in various fields. Professionals in fields such as engineering, finance, and computer science use the LCM in their daily work, whether it's optimizing algorithms, managing budgets, or scheduling projects. The ability to apply the LCM effectively is seen as a key competency for success in these and other fields.
Tips and Expert Advice
Practical Tips for Finding the LCM
Finding the LCM can be straightforward if you follow a few key tips. First, always start by understanding the definition of the LCM: it's the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given numbers. This understanding will guide you in choosing the most efficient method for finding the LCM.
Second, when dealing with small numbers, the listing multiples method can be quick and easy. Simply list the multiples of each number until you find a common multiple. For example, when finding the LCM of 3 and 4, list the multiples of 3 (3, 6, 9, 12, ...) and the multiples of 4 (4, 8, 12, ...). The first common multiple you encounter is the LCM.
Third, for larger numbers, the prime factorization method is often more efficient. Break down each number into its prime factors and then take the highest power of each prime factor that appears in any of the numbers. The product of these highest powers is the LCM. This method is particularly useful when dealing with numbers that have many factors.
Expert Advice on Applying the LCM
To effectively apply the LCM in real-world scenarios, it's important to recognize the underlying problem that the LCM can solve. Look for situations where you need to find a common point or interval that satisfies multiple conditions.
For example, in scheduling problems, identify the intervals at which different events occur and then find the LCM of those intervals. This will tell you when all the events will coincide. Similarly, in cooking, when adjusting recipes, use the LCM to find a common denominator for the ingredient ratios. This will help you maintain the correct proportions when scaling the recipe up or down.
Another piece of expert advice is to always check your answer to ensure that it makes sense in the context of the problem. The LCM should be a multiple of all the given numbers, and it should be the smallest such multiple. If your answer doesn't meet these criteria, double-check your calculations and make sure you haven't overlooked any factors.
Real-World Examples
Consider the following real-world examples to see how the LCM can be applied:
- Scheduling Meetings: Suppose you need to schedule a meeting with two colleagues who are available at different intervals. One colleague is available every 3 days, and the other is available every 4 days. To find the first day when both colleagues are available, you need to find the LCM of 3 and 4, which is 12. Therefore, the first day when both colleagues are available is 12 days from now.
- Dividing Snacks: You have 30 cookies and 40 candies, and you want to divide them equally among a group of friends. To find the largest number of friends you can share with, you need to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 30 and 40, which is 10. However, if you want to find the smallest number of packages you can buy so that you have an equal number of cookies and candies, you would use the LCM in a different way.
- Construction Project: You are building a fence using planks that are 3 inches wide and posts that are 4 inches wide. To ensure that the fence is evenly spaced, you need to find a common multiple of 3 and 4. The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12, so you can place a post every 12 inches to maintain even spacing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with the LCM, it's easy to make mistakes if you're not careful. One common mistake is confusing the LCM with the GCD. Remember that the LCM is the smallest common multiple, while the GCD is the largest common divisor. Make sure you understand the difference between these two concepts and use the appropriate method for each.
Another common mistake is overlooking factors when using the prime factorization method. Double-check your prime factorizations to ensure that you haven't missed any prime factors or exponents. It's also helpful to use a systematic approach, such as writing out all the prime factors in ascending order, to minimize the risk of errors.
Finally, always verify your answer by checking that it is a multiple of all the given numbers. If your answer is not a multiple of any of the numbers, you've made a mistake somewhere in your calculations. By avoiding these common mistakes and following the tips outlined above, you can confidently find and apply the LCM in a variety of contexts.
FAQ
Q: What is the LCM of 3 and 4? A: The LCM of 3 and 4 is 12. This means that 12 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 3 and 4 without leaving a remainder.
Q: How do you find the LCM of 3 and 4? A: There are several methods to find the LCM of 3 and 4. One common method is to list the multiples of each number until you find a common multiple. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, and so on. The smallest common multiple is 12.
Q: Why is the LCM important? A: The LCM is important because it helps solve problems in various fields, such as scheduling, cooking, construction, and mathematics. It provides a way to find a common point or interval that satisfies multiple conditions, making it a valuable tool for problem-solving and optimization.
Q: Can the LCM be used with more than two numbers? A: Yes, the LCM can be used with more than two numbers. To find the LCM of multiple numbers, you can use the prime factorization method or list the multiples of each number until you find a common multiple. The LCM will be the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given numbers.
Q: Is the LCM always larger than the numbers? A: The LCM is always greater than or equal to the largest of the given numbers. It can be equal to the largest number if that number is a multiple of all the other numbers. Otherwise, the LCM will be larger than the largest number.
Conclusion
In summary, the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics that helps find the smallest positive integer divisible by a set of numbers. For 3 and 4, the LCM is 12, a number easily derived through listing multiples, prime factorization, or using the GCD formula. Understanding the LCM is not just an academic exercise; it has numerous practical applications in everyday life, from scheduling events and adjusting recipes to optimizing construction projects.
Equipped with this knowledge, you can now tackle a variety of problems that require finding a common multiple. Whether you're planning a project, managing resources, or simply trying to divide snacks equally among friends, the LCM provides a valuable tool for simplifying complex tasks. Take the next step and apply this concept to your daily life. Try identifying situations where finding the LCM can help you streamline your activities. Share your experiences and insights with others, and let's explore the endless possibilities of mathematical problem-solving together.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Gallons In One Cubic Foot
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 6 Yards
Nov 30, 2025
-
How Many Yards Are In A Yard
Nov 30, 2025
-
Things That Start With An S
Nov 30, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 121
Nov 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.