What Is 100 In Roman Figure
catanddoghelp
Nov 19, 2025 · 10 min read
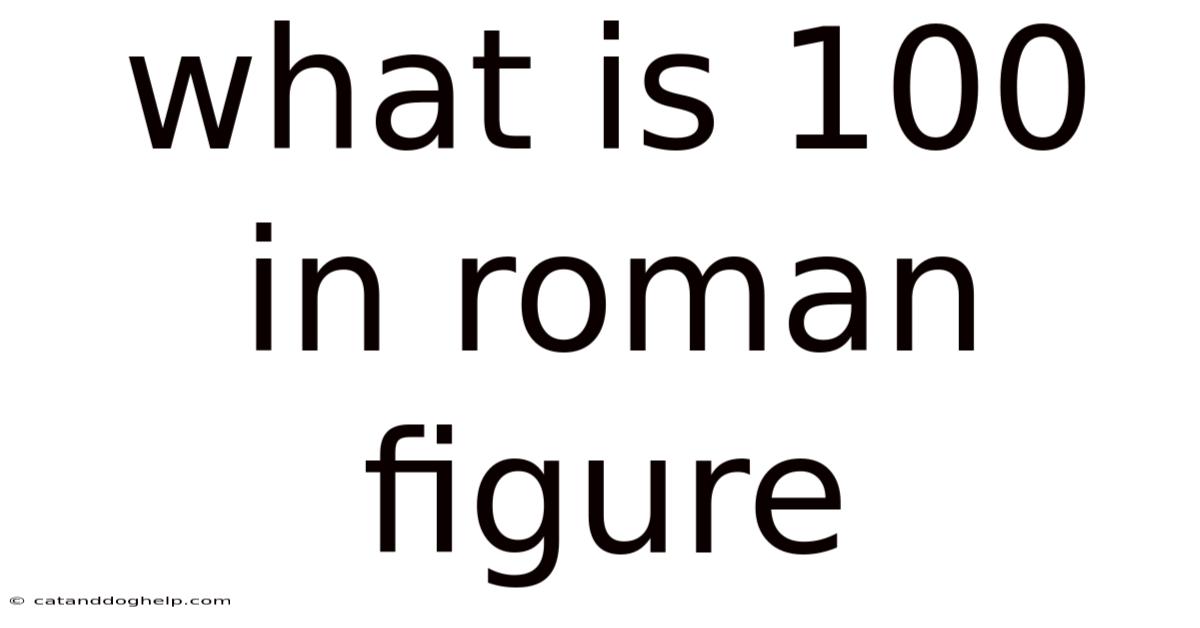
Table of Contents
Imagine stepping back in time to ancient Rome, where numbers weren't written as we know them today. Instead of the familiar '100', you'd encounter a single, powerful letter: 'C'. The Roman numeral system, with its elegant simplicity, continues to fascinate us, offering a glimpse into the intellectual world of one of history's greatest civilizations. But how did this system work, and why is 'C' the symbol for 100?
The Roman numeral 'C' isn't just a random assignment; it's steeped in history and practicality. Understanding its origins and how it fits into the broader Roman numeral system not only satisfies our curiosity but also enriches our appreciation for the mathematical ingenuity of the Romans. So, let's journey back to explore the world of Roman numerals and uncover the story behind 'C' and its significance as the representation of 100.
Main Subheading
The Roman numeral system, though different from our modern Arabic numeral system, was an effective method of counting and calculation used throughout the Roman Empire. It's based on a combination of letters from the Latin alphabet, each representing a specific numerical value. The system relies on addition and subtraction to create different numbers, making it both simple and versatile.
To fully appreciate the Roman numeral system, it's essential to understand the basic symbols and how they combine. The primary symbols are I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). By arranging these symbols in particular orders, the Romans could represent a wide range of numbers. For instance, placing a smaller value symbol before a larger one indicates subtraction (e.g., IV = 4), while placing it after indicates addition (e.g., VI = 6). This elegant system allowed the Romans to conduct trade, build infrastructure, and manage their vast empire with a practical and understandable method of numerical notation.
Comprehensive Overview
The Roman numeral system is more than just an ancient curiosity; it's a window into the Roman way of life. Understanding its definitions, scientific foundations, history, and essential concepts helps us appreciate its significance.
Definitions and Basic Principles
At its core, the Roman numeral system is based on seven symbols:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
These symbols are combined using the principles of addition and subtraction. Numbers are formed by adding the values of the symbols together, reading from left to right. For example, VIII represents 5 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 8. The subtractive principle comes into play when a smaller value symbol precedes a larger one, indicating subtraction. For instance, IV represents 5 - 1 = 4, and IX represents 10 - 1 = 9.
Scientific Foundations and Evolution
The Roman numeral system isn't based on a positional notation like the Arabic numeral system (where the position of a digit determines its value). Instead, it's an additive system with subtractive elements. This means that the order of symbols matters, but the value of each symbol remains constant regardless of its position.
Over time, the Roman numeral system evolved. Early forms of the system were more additive, with less emphasis on subtraction. The use of subtraction became more standardized during the Middle Ages, simplifying the representation of certain numbers and making the system more efficient.
History and Usage in Ancient Rome
The origins of Roman numerals can be traced back to the Etruscans, who inhabited the Italian Peninsula before the rise of Rome. The Romans adapted and refined the Etruscan system, developing it into the form we recognize today.
Roman numerals were used extensively throughout the Roman Empire for various purposes, including:
- Commerce: Recording transactions, prices, and quantities of goods.
- Construction: Marking distances, dimensions, and milestones on roads and buildings.
- Chronology: Dating events, inscriptions, and monuments.
- Military: Numbering legions and other military units.
The system's practicality and widespread use helped standardize it across the vast empire, making it an essential tool for administration and communication.
Understanding the Symbol 'C'
The symbol 'C' in Roman numerals represents the number 100. This association is believed to stem from the Latin word centum, which means "hundred." The Romans often used the first letter of a word to represent the quantity it described, making 'C' a natural choice for 100.
The adoption of 'C' as the symbol for 100 simplified the representation of larger numbers. Instead of writing multiple 'L's and 'X's, the Romans could use 'C' to denote 100, 'CC' for 200, and so on. This standardization made the system more efficient and easier to use.
Essential Concepts: Addition and Subtraction
The ability to both add and subtract values is crucial to understanding how Roman numerals work. Here are some examples:
- Addition:
- VI = 5 + 1 = 6
- XI = 10 + 1 = 11
- XV = 10 + 5 = 15
- LX = 50 + 10 = 60
- CX = 100 + 10 = 110
- Subtraction:
- IV = 5 - 1 = 4
- IX = 10 - 1 = 9
- XL = 50 - 10 = 40
- XC = 100 - 10 = 90
- CD = 500 - 100 = 400
- CM = 1000 - 100 = 900
These principles allow for the creation of a wide range of numbers using a limited set of symbols. The subtractive principle, in particular, allows for more concise representations of numbers like 4, 9, 40, 90, 400, and 900.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the Roman numeral system is no longer used for everyday calculations, it continues to appear in various contexts. Its enduring presence reflects its historical significance and aesthetic appeal.
Current Uses in the Modern World
Today, Roman numerals are commonly used in:
- Clock Faces: Many traditional clocks and watches use Roman numerals to mark the hours.
- Book Chapters and Prefaces: Roman numerals are often used to number the preliminary pages of books or to denote chapter numbers.
- Movie Sequels and Events: Film series (e.g., Rocky II, Rambo IV) and major events (e.g., Super Bowl XLV, Olympic Games XXIX) often use Roman numerals to indicate sequential order.
- Building Cornerstones and Monuments: Roman numerals are frequently used to inscribe dates on buildings, monuments, and cornerstones, adding a touch of classical elegance.
- Outlines and Lists: In academic and professional settings, Roman numerals are sometimes used to organize outlines or lists.
Data and Popular Opinions
The persistence of Roman numerals in these contexts reflects a blend of tradition and aesthetics. Many people appreciate the classic and timeless quality that Roman numerals bring to designs and inscriptions. In surveys and polls, respondents often express a preference for Roman numerals in certain applications, particularly where a sense of history or formality is desired.
Professional Insights
From a design perspective, Roman numerals offer a unique visual appeal. Their simple, geometric forms can complement a variety of styles, from traditional to modern. The use of Roman numerals in branding and design can evoke a sense of sophistication and heritage, making them a valuable tool for conveying a particular image or message.
From an educational standpoint, understanding Roman numerals provides a valuable link to the past. Learning about the system can enhance one's appreciation for history, mathematics, and the evolution of numerical notation. It also encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as converting between Roman numerals and Arabic numerals requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of the underlying principles.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering Roman numerals can seem daunting at first, but with a few practical tips and some expert advice, anyone can become proficient in their use.
Learn the Basic Symbols
The first step is to memorize the values of the seven basic symbols: I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000). Having these values firmly in mind will make it much easier to decode and construct Roman numerals.
For example, when you see 'MCMLXXXIV', start by recognizing 'M' as 1000, 'CM' as 900 (1000 - 100), 'LXXX' as 80 (50 + 10 + 10 + 10), and 'IV' as 4 (5 - 1). Combining these values, you get 1000 + 900 + 80 + 4 = 1984. Familiarity with the basic symbols is the foundation upon which all other understanding is built.
Understand the Rules of Addition and Subtraction
The core of the Roman numeral system lies in the rules of addition and subtraction. Remember that when a symbol of smaller value appears before a symbol of larger value, you subtract the smaller value from the larger one. Conversely, when a symbol of smaller value appears after a symbol of larger value, you add the smaller value to the larger one.
For instance, in the numeral 'XIV', the 'X' represents 10, and the 'IV' represents 4 (5 - 1). Therefore, XIV = 10 + 4 = 14. On the other hand, in the numeral 'XVI', the 'X' represents 10, and the 'VI' represents 6 (5 + 1). So, XVI = 10 + 6 = 16. Practice identifying these patterns to quickly and accurately interpret Roman numerals.
Follow the Rule of Three
A key rule to remember is that a symbol can be repeated up to three times in a row, but no more. For example, 'III' represents 3, 'XXX' represents 30, and 'CCC' represents 300. However, you cannot write 'IIII' for 4; instead, you use the subtractive principle and write 'IV'. Similarly, you can't write 'XXXX' for 40; you use 'XL' instead.
This rule helps maintain clarity and avoids unnecessarily long sequences of symbols. By adhering to the rule of three, you ensure that your Roman numeral representations are both accurate and concise.
Break Down Large Numbers
When dealing with larger numbers, it can be helpful to break them down into smaller, more manageable components. Start by identifying the largest possible symbol that can be used, then work your way down.
For example, to convert 1944 to Roman numerals, begin with the largest symbol less than 1944, which is 'M' (1000). Subtract 1000 from 1944, leaving 944. The largest symbol less than 944 is 'CM' (900), so subtract that, leaving 44. Now, you have 'XL' (40) and 'IV' (4), giving you 'MCMXLIV'. Breaking down the number into smaller parts makes the conversion process much easier and less prone to errors.
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, proficiency in Roman numerals comes with practice. Try converting numbers from Arabic numerals to Roman numerals, and vice versa. You can find practice exercises online or create your own.
Start with simple numbers and gradually work your way up to more complex ones. The more you practice, the more familiar you will become with the symbols and the rules, and the faster and more accurately you will be able to work with Roman numerals. Regular practice is the key to mastery.
FAQ
Q: Why is 'C' used for 100 in Roman numerals?
A: 'C' is used for 100 because it is the first letter of the Latin word centum, which means "hundred."
Q: What are the basic symbols in the Roman numeral system?
A: The basic symbols are I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000).
Q: How do you represent 4 and 9 in Roman numerals?
A: 4 is represented as IV (5 - 1), and 9 is represented as IX (10 - 1).
Q: Can a symbol be repeated more than three times in a row?
A: No, a symbol can be repeated up to three times in a row, but no more. For example, 3 is III, but 4 is IV, not IIII.
Q: How do you convert a large number like 1984 into Roman numerals?
A: To convert 1984, break it down: M (1000) + CM (900) + LXXX (80) + IV (4) = MCMLXXXIV.
Conclusion
Understanding that 'C' stands for 100 in Roman numerals is just the beginning of a fascinating journey into an ancient numerical system. The Roman numeral system, with its blend of addition and subtraction, offers a unique perspective on how numbers can be represented and used. From its historical roots to its modern-day applications, the system continues to captivate and intrigue.
Now that you have a solid understanding of Roman numerals, especially the significance of 'C', why not put your knowledge to the test? Try converting significant dates, like your birth year, into Roman numerals. Share your results and any interesting facts you discover in the comments below. Let's keep the conversation going and further explore the rich history and enduring appeal of Roman numerals!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
6 Letter Words Starting With E
Nov 20, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 56
Nov 20, 2025
-
Which Element Has The Highest Electronegativity
Nov 20, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 10
Nov 20, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 9
Nov 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 100 In Roman Figure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.